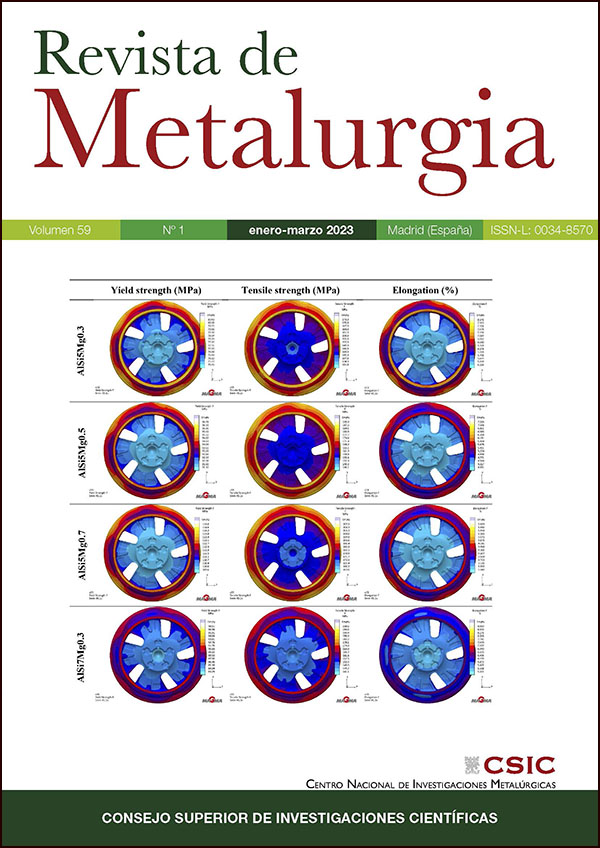
Investigation of metallurgical properties of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys with integrated computational materials engineering for wheel production
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3989/revmetalm.233Keywords:
Aluminum alloys, Integrated computational materials engineering, Low pressure die casting, Mechanical properties, SimulationAbstract
In this study, integrated computational materials engineering, which is one of the new generation approaches in materials science, was used in the production of aluminum alloy wheels by low pressure die casting method. In casting alloys, the efficiency of grain refinement provided by master alloys added to the melt decreases with increasing silicon content of the alloy. In this context, as-cast properties of silicon reduced (Si: 5.0 wt.%) alloys with different Mg ratios (Mg: 3.0, 5.0, 7.0 wt.%) are discussed using integrated computational materials engineering approaches. It has been evaluated whether the examined alloys can be an alternative to the AlSi7Mg0.3 alloy, which is currently used traditionally in the production of aluminum-based wheels, with their microstructural and mechanical properties. The study consists of three stages which are computer-aided production, pilot production, testing and characterization studies. In computer-aided production, original sub-eutectic compositions were determined in types and amounts of alloying elements, alloy designs were realized and a database was created with a computational materials engineering software. Then, low pressure die casting analysis were performed in a virtual environment by transferring these data directly to the casting simulation software. Thus, the microstructural and mechanical properties of the wheel were obtained computationally on the basis of the varying alloy composition. In the second stage, the virtually designed alloy compositions were prepared and sample wheels were manufactured by the low pressure die casting method on an industrial scale. In the testing and characterization phase, spectral analyses, macro and microstructural examinations, hardness measurements and tensile tests were carried out. As a result of this study, it was determined that the studied alloys could be used in the production of wheels by the low pressure die casting method considering the metallurgical properties expected from the wheel. In addition, it is thought that the mathematical design of the material with integrated computational materials engineering approaches before casting simulations will play an active role in the competitiveness and sustainability of the aluminum industry in technological conditions.
Downloads
References
Allison, J., Backman, D., Christodoulou, L. (2006). Integrated computational materials engineering: A new paradigm for the global materials profession. JOM 58, 25-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-006-0223-5
Andersson, J.O., Helander, T., Höglund, L., Shi, P., Sundman, B. (2002). Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, computational tools for materials science. CALPHAD 26 (2), 273-312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0364-5916(02)00037-8
Atasoy, Ö.A. (1990). Eutectic Alloys: Solidification Mechanisms and Applications. Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul.
Campbell, J. (2003). Castings. 2nd Edition, Londra: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Eby, F.J., Narayanan, S.A., Abhiram, R., Navaneeth, M.V., Manu, K., Shankar, K.V., Nidhin, A.R. (2022). Influence of solutionising time on the dendrite morphology and mechanical behaviour of Al-Si-Mg-Ni hypoeutectic alloy. Silicon 14 (12), 6749-6760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01401-z
Fayomi. O.S.I., Popoola. A.P.I., Udoye. N.E. (2017). Effect of alloying element on the integrity and functionality of aluminium-based alloy. In Aluminium Alloys - Recent Trends in Processing, Characterization, Mechanical Behavior and Applications. 13, pp. 243-262. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.71399
Flemings, M.C., Riek, R.G., Young, K.P. (1976). Rheocasting. Mater. Sci. Eng. 25, 103-117. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5416(76)90057-4
Fortini. A., Merlin. M., Fabbri. E., Pirletti. S., Garagnani. G.L. (2016). On the influence of Mn and Mg additions on tensile properties. microstructure and quality index of the A356 aluminum foundry alloy. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2, 2238-2245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostr.2016.06.280
Guo, Z., Sha, W. (2005). Quantification of precipitate fraction in Al-Si-Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 392 (1-2). 449-452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.09.020
Guofa, M., Xiangyu, L., Kuangfei, W., Hengzhi, F. (2009). Numerical simulation of low pressure Die-Casting aluminum wheel. China Foundry 6 (1), 48-52.
Ji, S., Yang, W., Gao, F., Watson, D., Fan, Z. (2013). Effect of iron on the microstructure and mechanical property of Al-Mg-Si-Mn and Al-Mg-Si diecast alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 564, 130-139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.11.095
Jolly, M., Katgerman, L. (2022). Modelling of defects in aluminium cast products. Prog. Mater. Sci. 123, 100824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2021.100824
Khan, M.A.A., Sheikh, A.K., Asad, M. (2020). Mold design and casting of an impeller using MAGMASoft. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 9 (12), 1579-1583. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijmerr.9.12.1579-1583
Kumar, V., Mehdi, H., Kumar, A. (2015). Effect of silicon content on the mechanical properties of aluminum alloy. Int. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 2 (4), 1326-1330.
Lumley. R. (2011). Fundamentals of aluminium metallurgy. Wood Publishing Limited, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857090256
Mukund, A., Nair, A.S., Nived, S., Raagavendran, R., Premkumar, A., Raj, A.N., Shankar, K.V. (2020). Impact of solutionising temperature on the microstructure, hardness and tensile strength of Al-6.6Si-0.3Mg-3Ni alloys. Mater. Today: Proc. 38 (5), 2117-2122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.725
Mulazimoglu, M.H., Drew, R.A.L., Gruzleski, J.E. (1989). The electrical conductivity of cast Al−Si alloys in the range 2 to 12.6 wt pct silicon. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 20, 383-389. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02653917
Narayanan, L.A., Samuel, F.H., Gruzleski, J.E. (1994). Crystallization behavior of iron containing intermetallics compounds in 319 aluminum alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 25, 1761-1773. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02668540
Ovrutsky, A.M. Prokhoda, A.S., Rasshchupkyna, M.S. (2014). Computational Materials Science, Computer Modeling of Physical Phenomena and Processes. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-420143-9.00001-6
Patnaik, L., Saravanan, I., Kumar, S. (2020). Die casting parameters and simulations for crankcase of automobile using MAGMASoft. Mater. Today: Proc. 22 (3), 563-571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.08.208
Schäfer, M. (2006). Computational engineering-introduction to numerical methods. Berlin, Springer-Verlag.
Stadler, F., Antrekowitsch. H., Fragner. W., Kaufmann. H., Pinatel. E.R., Uggowitzer. P.J. (2013). The effect of main alloying elements on the physical properties of Al-Si foundry alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 560, 481-491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.09.093
Şimşek, İ., Özyürek, D. (2019). Investigation of the effects of Mg amount on microstructure and wear behavior of Al-Si-Mg alloys. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 22 (1), 370-375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2018.08.016
Thapliyal, S., Komarasamy, M., Shukla, S., Zhou, L., Hyer, H., Park, S., Sohn, Y., Mishra, R.S. (2020). An integrated computational materials engineering-anchored closed-loop method for design of aluminum alloys for additive manufacturing. Materialia 9, 100574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2019.100574
Thornton, K., Nola, S., Edwin Garcia, R., Asta, M., Olso, G.B. (2009). Computational materials science and engineering education: A survey of trends and needs. JOM 61, 12-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-009-0142-3
Timpel, M., Wanderka, N., Schlesiger, R., Yamamoto, T., Lazarev, N., Isheim, D., Schmitz, G., Matsumura, S., Banhart, J. (2012). The role of strontium in modifying aluminium-silicon alloys. Acta Mater. 60 (9), 3920-3928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.03.031
Wang, W.Y., Li, J., Liu, W., Liu, Z. (2019). Integrated computational materials engineering for advanced materials: A brief review. Comput. Mater. Sci. 158, 42-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2018.11.001
Yağcı, T., Cöcen, Ü., Çulha, O. (2021). Aluminum alloy development for wheel production by low pressure die casting with new generation computational materials engineering approaches. Arch. Foundry Eng. 21 (4), 35-46.
Yamashita, J., Hayakawa, H. (1976). Deviations from Matthiessen's rule in electrical resistivity of nickel-based alloys. Prog. Theor. Phys. 56 (2), 361-374. https://doi.org/10.1143/PTP.56.361
Zou, G., Chai, Y., Shen, Q., Cheng, T., Zhang, H. (2022). Analysis of the fluidity and hot tearing susceptibility of AlSi3.5Mg0.5Cu0.4 and A356 aluminum alloys. Inter. Metalcast. 16, 909-923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00649-w
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
© CSIC. Manuscripts published in both the printed and online versions of this Journal are the property of Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, and quoting this source is a requirement for any partial or full reproduction.All contents of this electronic edition, except where otherwise noted, are distributed under a “Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International” (CC BY 4.0) License. You may read here the basic information and the legal text of the license. The indication of the CC BY 4.0 License must be expressly stated in this way when necessary.
Self-archiving in repositories, personal webpages or similar, of any version other than the published by the Editor, is not allowed.
Funding data
Manisa Celal Bayar Üniversitesi
Grant numbers 2018-182